Sildenafil (Viagra);

Overview
Sildenafil, a groundbreaking medication, revolutionized the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED) since its introduction.
Top Brands of sildenafil:
Renowned pharmaceutical companies produce sildenafil under various brand names. Among the most notable are Viagra, Revatio, and Suhagra. Each brand maintains the same active ingredient, ensuring efficacy and reliability.
What does Viagra (Sildenafil) Do?
Sildenafil operates by inhibiting the enzyme phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5), which facilitates the degradation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). This inhibition prolongs the effects of cGMP, promoting smooth muscle relaxation, vasodilation, and increased blood flow to the corpus cavernosum, facilitating penile erection.
Uses of Sildenafil:
1. Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Sildenafil is widely prescribed for the management of erectile dysfunction (ED) in men. The recommended starting dose for most men is 50mg, taken approximately one hour before sexual activity. Depending on individual response and tolerance, the dose can be adjusted to 25mg or increased to 100mg. It’s essential to take sildenafil on an empty stomach for optimal absorption, as fatty foods can delay its onset of action. The medication typically remains effective for up to four to six hours, allowing for spontaneous sexual activity within this timeframe.
2. Management of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
Under the brand name Revatio, sildenafil is utilized in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), a condition characterized by high blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs. In this context, the recommended dose of sildenafil is lower compared to its use for erectile dysfunction. Patients typically start with a dose of 20mg, taken three times daily. Depending on individual response and tolerability, the dose may be increased to 40mg three times daily. Sildenafil helps to improve exercise capacity, relieve symptoms, and slow down the progression of PAH by dilating the blood vessels in the lungs, reducing pulmonary arterial pressure, and easing the workload on the heart.
Both indications of sildenafil require careful consideration of patient factors such as age, overall health, concomitant medications, and presence of underlying medical conditions. It’s crucial for healthcare providers to assess each patient individually and tailor the dose accordingly to achieve optimal therapeutic outcomes while minimizing the risk of adverse effects. Regular monitoring and follow-up visits are essential to ensure the continued safety and efficacy of sildenafil therapy for both erectile dysfunction and pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Doses
The recommended dosage of sildenafil varies based on the condition being treated. For erectile dysfunction, a typical starting dose is 50mg, taken approximately one hour before sexual activity, with adjustments made according to individual response. In cases of pulmonary arterial hypertension, doses are lower, typically ranging from 20mg to 40mg taken three times daily.
Interactions of sildenafil with Other Drugs:
Sildenafil, while generally safe and effective when used as prescribed, can interact with certain medications, potentially leading to adverse effects or reduced efficacy. It’s crucial for healthcare providers and patients to be aware of these interactions to minimize risks and ensure optimal treatment outcomes. Here are some notable drug interactions involving sildenafil:
1. Nitrates and Nitric Oxide Donors:
Sildenafil should not be taken concomitantly with nitrates or nitric oxide donors, such as nitroglycerin, isosorbide dinitrate, or amyl nitrate. The combination can lead to a dangerous drop in blood pressure, causing symptoms of hypotension such as dizziness, fainting, or even cardiac events. Patients should avoid using sildenafil if they are taking medications containing nitrates, commonly prescribed for the treatment of angina or chest pain.
2. Alpha-Blockers:
Alpha-blockers, medications used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), can potentiate the hypotensive effects of sildenafil. Combining sildenafil with alpha-blockers may result in symptomatic hypotension, characterized by lightheadedness, fainting, or orthostatic hypotension (a drop in blood pressure upon standing). Dosage adjustments may be necessary when using these medications together, and close monitoring is recommended.
3. Protease Inhibitors:
Protease inhibitors, a class of antiretroviral medications used to treat HIV/AIDS, can increase the plasma levels of sildenafil, potentially intensifying its effects and increasing the risk of adverse reactions. Patients taking protease inhibitors should use sildenafil cautiously, starting with a lower dose and monitoring for signs of excessive drug effects, such as prolonged erections or hypotension.
4. Certain Antibiotics and Antifungal Medications:
Some antibiotics and antifungal medications, particularly erythromycin, clarithromycin, ketoconazole, and itraconazole, can inhibit the metabolism of sildenafil, leading to increased plasma concentrations and a higher risk of adverse effects. Healthcare providers should consider dosage adjustments or alternative treatments when prescribing sildenafil to patients concurrently taking these medications.
5. Other Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors:
Concurrent use of sildenafil with other phosphodiesterase inhibitors, such as tadalafil (Cialis) or vardenafil (Levitra), may potentiate the pharmacological effects of both drugs, increasing the risk of adverse reactions such as hypotension or priapism (prolonged erection). Patients should avoid using multiple phosphodiesterase inhibitors simultaneously unless under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Contraindications and Special Precautions for Sildenafil Use:
Sildenafil is a potent medication used primarily for the treatment of erectile dysfunction and pulmonary arterial hypertension. While generally safe and effective, there are certain contraindications and special precautions that healthcare providers must consider before prescribing sildenafil to ensure patient safety and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
1. Hypersensitivity:
Sildenafil is contraindicated in individuals with a known hypersensitivity to the drug or any of its components. Patients who experience allergic reactions such as rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing after taking sildenafil should discontinue use and seek medical attention immediately.
2. Cardiovascular Disease:
Sildenafil should be used with caution in patients with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions, including coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, or unstable angina. The medication can potentiate the hypotensive effects of nitrates and alpha-blockers, leading to a significant drop in blood pressure and cardiovascular complications. Patients with a recent history of heart attack, stroke, or life-threatening arrhythmias should avoid sildenafil use.
3. Uncontrolled Hypertension:
Sildenafil can exacerbate hypertension and increase the risk of cardiovascular events in patients with uncontrolled high blood pressure. Healthcare providers should carefully assess blood pressure levels and consider alternative treatment options for individuals with poorly controlled hypertension.
4. Liver or Kidney Dysfunction:
Patients with severe hepatic impairment (liver dysfunction) or end-stage renal disease (kidney dysfunction) may experience prolonged elimination half-life and increased plasma concentrations of sildenafil. Dosage adjustments may be necessary in these populations to avoid drug accumulation and potential toxicity.
5. Priapism:
Sildenafil has been associated with the development of priapism, a prolonged and painful erection lasting more than four hours. Patients with a history of priapism or conditions predisposing them to priapism, such as sickle cell anemia or leukemia, should use sildenafil with caution and seek prompt medical attention if an erection persists beyond the recommended duration.
6. Retinal Disorders:
Sildenafil may cause visual disturbances, including changes in color vision or blurred vision, due to its effects on phosphodiesterase type 6 (PDE6) in the retina. Patients with pre-existing retinal disorders such as retinitis pigmentosa should exercise caution when using sildenafil and undergo regular ophthalmologic assessments to monitor for any changes in vision.
7. Gastric Ulcers or Bleeding Disorders:
Sildenafil can increase gastric acid secretion and may exacerbate gastric ulcers or gastrointestinal bleeding in susceptible individuals. Patients with a history of peptic ulcers, bleeding disorders, or concurrent use of anticoagulant medications should use sildenafil with caution and report any signs of gastrointestinal bleeding or ulceration to their healthcare provider.
Side Effects of Sildenafil
Sildenafil, like any medication, can elicit a range of side effects, although not everyone experiences them. Understanding these potential adverse reactions is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients to ensure safe and effective treatment. Here are some common and less common side effects associated with sildenafil use:
Common Side Effects:
- Headache: One of the most common side effects of sildenafil is headache, which may occur shortly after taking the medication and usually resolves on its own.
- Flushing: Sildenafil can cause facial flushing or redness, often accompanied by warmth or tingling sensations, due to its vasodilatory effects on blood vessels.
- Dyspepsia: Some individuals may experience indigestion, heartburn, or gastrointestinal discomfort after taking sildenafil, particularly when consumed with food.
- Nasal Congestion: Sildenafil may cause nasal congestion or stuffiness, leading to a sensation of blocked or runny nose.
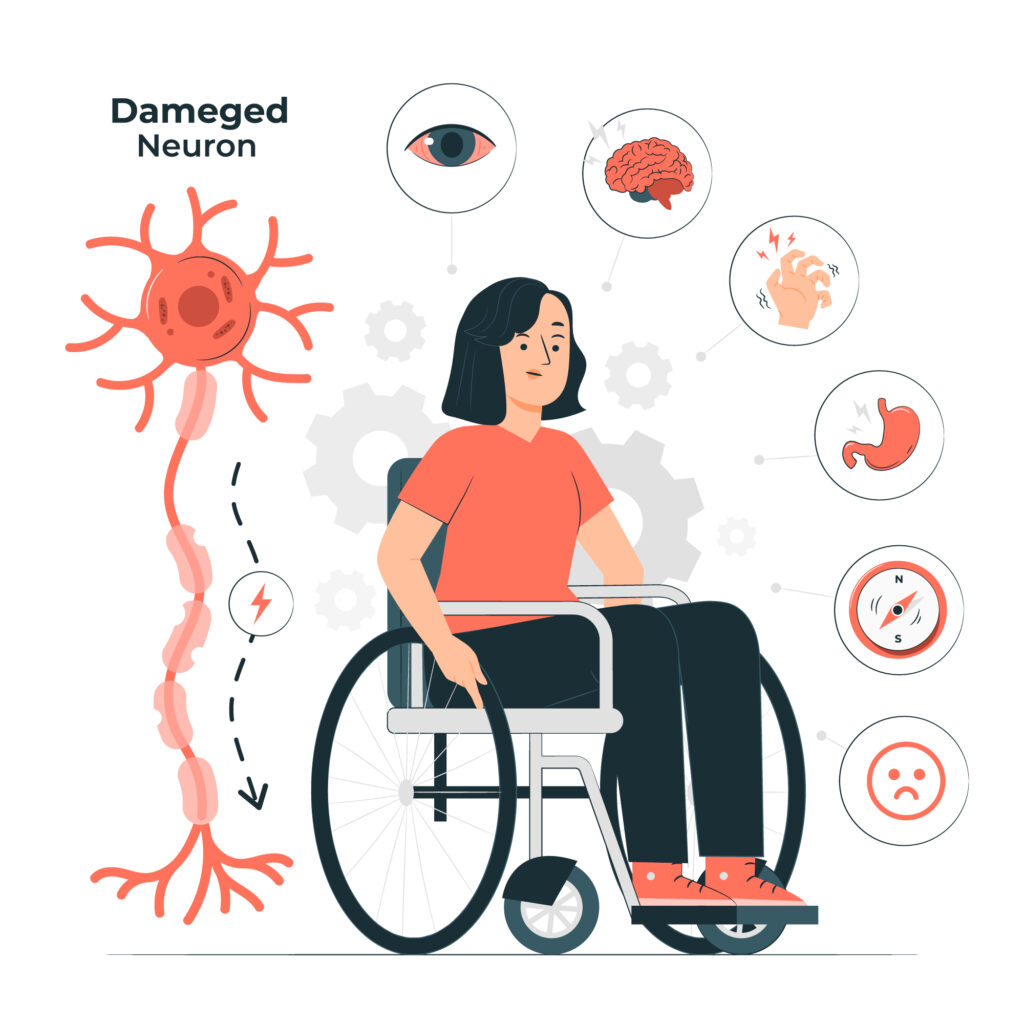
- Visual Disturbances: Changes in vision, such as blurred vision, sensitivity to light, or alterations in color perception (e.g., blue-tinged vision), can occur with sildenafil use, albeit less frequently.
Less Common Side Effects:
- Priapism: While rare, sildenafil has been associated with priapism, a prolonged and painful erection lasting more than four hours. Priapism requires immediate medical attention to prevent tissue damage and permanent erectile dysfunction.
- Hearing Changes: In some cases, sildenafil use has been linked to sudden hearing loss or changes in auditory perception. Patients experiencing any hearing abnormalities while taking sildenafil should seek medical evaluation promptly.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Sildenafil can cause dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting, particularly when standing up from a sitting or lying position. These symptoms may be exacerbated by alcohol consumption or concurrent use of certain medications.
- Muscle Aches: Some individuals may experience muscle aches or pains, particularly in the back, limbs, or joints, as a rare side effect of sildenafil.
- Skin Reactions: Allergic skin reactions, such as rash, itching, or hives, may occur in susceptible individuals following sildenafil administration. Severe allergic reactions, though rare, require immediate medical attention.