Frostbite;
Overview:
Frostbite is a severe cold-related injury characterized by freezing of the skin and underlying tissues, often occurring in extreme cold conditions. Understanding the causes, signs, stages, and treatment of frostbite is crucial for mitigating its effects and preventing long-term complications.
What is Frostbite?
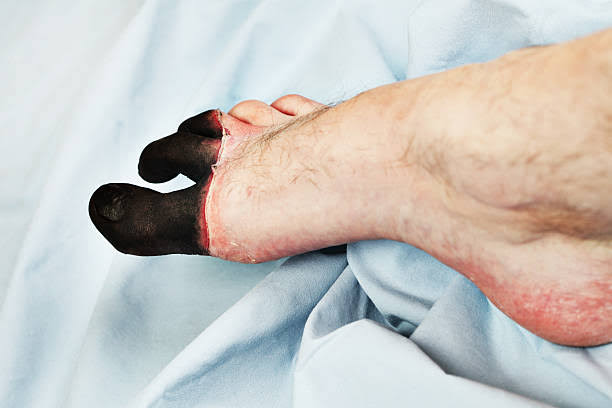
Frostbite occurs when exposure to cold temperatures causes freezing of the skin and underlying tissues. Prolonged exposure to cold, wind, and moisture increases the risk of frostbite, especially in vulnerable areas such as fingers, toes, ears, nose, and cheeks.
Causes:
- Cold Exposure: Exposure to freezing temperatures, particularly for extended periods, is the primary cause of frostbite.
- Wind Chill: Wind increases the rate of heat loss from the body, accelerating the onset of frostbite even at relatively mild temperatures.
- Moisture: Wet or damp conditions exacerbate heat loss from the body, increasing the risk of frostbite, especially when combined with cold temperatures.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Numbness: The affected area may feel cold and numb, with diminished sensation.
- Skin Discoloration: The skin may appear pale, white, or grayish-yellow, indicating reduced blood flow and tissue damage.
- Tingling or Burning Sensation: As frostbite progresses, individuals may experience tingling, burning, or throbbing pain in the affected area.
- Hardening of Tissues: The skin and underlying tissues may feel firm or hard to the touch, indicating freezing of the tissues.
- Blister Formation: In severe cases, fluid-filled blisters may develop upon rewarming of the affected area.
Stages:
- Frostnip: The mildest form of frost-bite, characterized by superficial freezing of the skin and tissues without permanent damage.
- Superficial Frostbite: Involves freezing of the skin and superficial tissues, resulting in numbness, tingling, and discoloration.
- Deep Frostbite: Affects deeper tissues, including muscles, tendons, and blood vessels, leading to waxy, white, or bluish-purple skin, loss of sensation, and potential tissue death.
Risk Factors:
- Exposure Time: Prolonged exposure to cold increases the risk of frost-bite, especially without adequate protection.
- Age: Infants, children, and older adults are more susceptible to frost-bite due to differences in thermoregulation and circulation.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, and Raynaud’s disease, can impair circulation and increase the risk of frostbite.
- Alcohol and Tobacco Use: Alcohol consumption and tobacco use can impair peripheral circulation, reducing the body’s ability to withstand cold temperatures and increasing the risk of frost bite.
Treatment of Frostbite:
- Move to Warmth: Immediately move to a warm environment to prevent further tissue damage.
- Remove Wet Clothing: Remove wet clothing and gently dry the affected area to prevent further heat loss.
- Gradual Rewarming: Rewarm frostbitten areas gradually by immersing them in warm water or applying warm compresses.
- Protect Blisters: If blisters develop, leave them intact to reduce the risk of infection and cover with sterile dressings.
- Seek Medical Attention: Severe cases of frost-bite require medical evaluation and treatment to prevent complications such as tissue loss or infection.
Complications of frostbite:
- Tissue Necrosis: Severe frost-bite can lead to tissue death (gangrene), requiring surgical intervention or amputation.
- Infection: Frostbitten tissues are prone to infection, which can spread rapidly without prompt medical treatment.
- Long-Term Sensory Loss: Permanent loss of sensation or function may occur in severely frostbitten areas, affecting mobility and quality of life.
Conclusion:
Frost-bite is a serious cold-related injury that can lead to tissue damage, long-term complications, and even permanent disability if left untreated. By understanding the causes, signs, stages, and treatment of frost-bite, individuals can take proactive measures to protect themselves and others from the chilling effects of cold exposure. Whether venturing into wintry landscapes or facing cold weather at home, prioritizing safety and preparedness is paramount in navigating the icy terrain of frostbite.
Read more:

