Causes of diabetes mellitus;
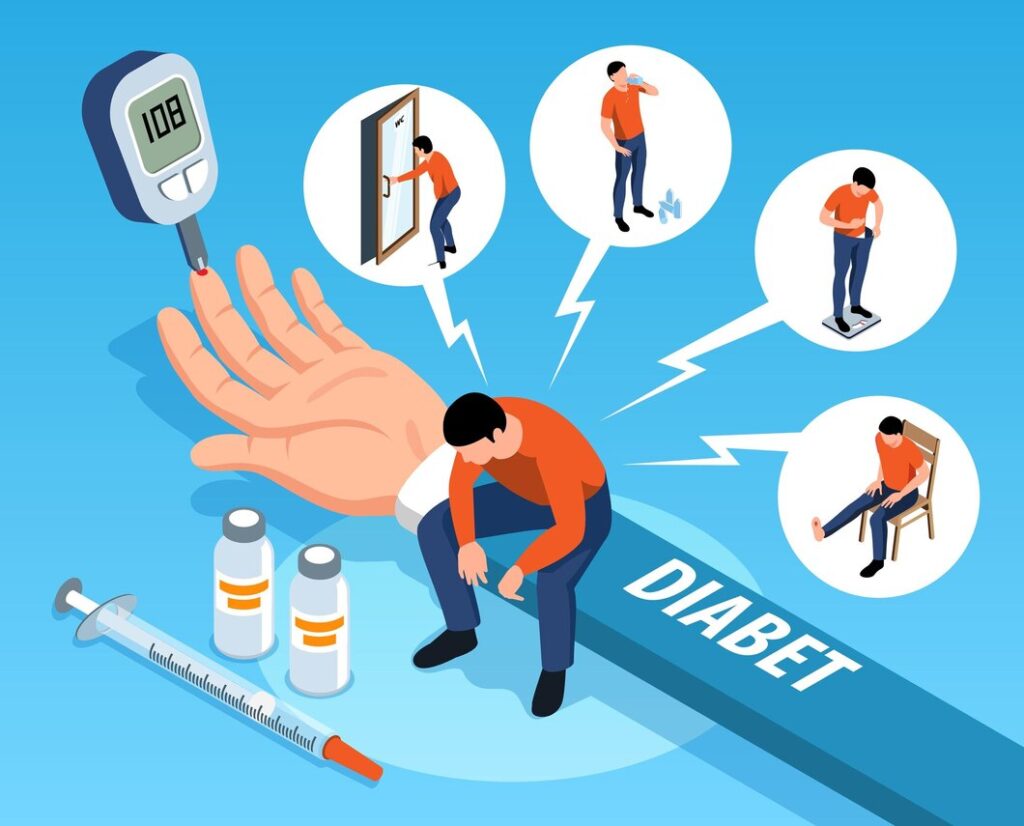

Introduction
Diabetes Mellitus is a multifaceted metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels, with insulin resistance playing a pivotal role in its pathogenesis.
Causes of Diabetes Mellitus:
1. causes of Diabetes –Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
– Genetic Predisposition:
- Individuals with a family history of Type 1 diabetes are at a higher risk.
- Specific genes, such as those in the HLA complex, play a crucial role in immune-mediated destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
– Autoimmune Response:
- Type 1 diabetes is primarily an autoimmune disorder, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells.
- Environmental triggers, such as viral infections, may activate the autoimmune response in genetically susceptible individuals.
2. Causes of Diabetes – Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
– Insulin Resistance:
- Insulin resistance occurs when cells in the body become less responsive to the action of insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
- Obesity, physical inactivity, and genetic factors contribute to insulin resistance.
– Pancreatic Dysfunction:
- Over time, the pancreas may fail to produce enough insulin to meet the body’s demands, exacerbating insulin resistance.
- Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress within the pancreas contribute to beta-cell dysfunction.
3. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
– Hormonal Changes:
- During pregnancy, hormonal changes can lead to insulin resistance, particularly in the later stages of gestation.
- Hormones produced by the placenta, such as human placental lactogen and cortisol, contribute to insulin resistance.
Rare Types of Diabetes Mellitus
- Genetic Mutations:
- MODY, NDM, Wolfram Syndrome, mitochondrial diabetes, and FCPD are rare forms of diabetes caused by genetic mutations affecting insulin production, pancreatic function, or mitochondrial DNA.
Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance
– Cellular Signaling Dysfunction:
- Insulin binds to receptors on cell surfaces, initiating a signaling cascade that promotes glucose uptake.
- Defects in intracellular signaling pathways impair the ability of cells to respond to insulin effectively.
– Downregulation of Insulin Receptors:
- Prolonged exposure to high insulin levels can lead to downregulation of insulin receptors on cell surfaces, reducing sensitivity to insulin.
– Inflammatory Pathways:
- Chronic inflammation associated with obesity disrupts insulin signaling pathways, contributing to insulin resistance.
- Inflammatory cytokines released by adipose tissue and immune cells further impair insulin action.
Consequences of Insulin Resistance
- Hyperglycemia:
- Insulin resistance impairs glucose uptake by cells, leading to elevated blood glucose levels and promoting the development of diabetes.
- Dyslipidemia and Hypertension:
- Insulin resistance is often accompanied by dyslipidemia and hypertension, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Risk Factors for Insulin Resistance
- Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle:
- Excess adipose tissue and physical inactivity are significant risk factors for insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes.
- Genetic Predisposition:
- Genetic factors contribute to individual susceptibility to insulin resistance and diabetes.
Summary:
The intricate interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors contributes to the development of diabetes Mellitus and insulin resistance.
Read More: